Type 4.2: 推斷一個人既genotype (sex-linked)
再講4.2 通常都係考X-linked recessive 既trait。解決呢類要記住先前講過既兩句口訣。 1. 相生相剋 2. 異性相吸 今次有啲特別,可以淨係用第一句,或者用曬兩句都得。淨係用第一句就係搵出有吾同phenotype既母女。兩句用曬即係搵一pair 有吾同phenotype 既父女或母子。再由有個trait 既individual (叫呢個人做A),再去到同A有吾同phenotype 既individual (叫呢個人做B) B 係heterozygous
Formula of case 1:
- (Being a sex-linked trait, the allele for the trait is located on the X-chromosome.)
- Genotype of female is XX. A has the trait. She must have two X-chromosomes with the recessive alleles for the trait i.e. she is homozygous recessive for the trait.
- One of her X-chromosomes with the recessive allele must have been inherited to / from B.
- B is normal in phenotype. Therefore, she must have an X-chromosome with the dominant normal allele.
- Therefore, B is heterozygous.
Formula of case 2:
- (Being a sex-linked trait, the allele for the trait is located on the X-chromosome.)
- As A has the trait, he must have an X-chromosome with the recessive allele for the trait.
- This X-chromosome must have been inherited from / to B.
- Genotype of female is XX. As B is normal, she must have at least one X-chromosome with the dominant normal allele.
- Therefore, B is heterozygous.
至於使吾使寫做allele 係 X chromosome 度就要睇情況,如果題目冇寫到個trait係X-linked,淨係講再個trait係咩e.g. Colour blindness ,或者淨係講個trait係sex-linked 就要落呢句。
e.g. 1 1996 HKCE Human Biology I (1aiii: modified)
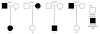
The diagram below shows a pedigree for the inheritance of a human genetic disease.
From part (i), the disease is recessive and from (ii), the disease is sex-linked. Deduce, with reasons, the genotype of individual 2.
- Genotype of female is XX. 5 has the disease. She must have two X-chromosomes with the recessive alleles for the trait i.e. she is homozygous recessive for the trait.
- One of her X-chromosomes with the recessive allele must have been inherited from individual 2.
- Individual 2 is normal in phenotype. Therefore, she must have an X-chromosome with the dominant normal allele.
- Therefore, individual 2 is heterozygous.
e.g. 2 2012 HKDSE PP IB (9bi)
The female (B) has a family history of colour blindness. The son (E) has colour blindness. The pedigree of this family is shown in the following diagram:
In humans, colour blindness is a sex-linked trait. Based on the above pedigree, deduce the genotype of the mother (B) with respect to colour vision.
- Being a sex-linked trait, the allele for colour blindness is located on the X-chromosome.
- As individual E has colour blindness, he must have an X-chromosome with the recessive allele for colour blindness.
- This X-chromosome must have been inherited from his mother B.
- Genotype of female is XX. As the mother is normal, she must have at least one X-chromosome with the dominant normal allele for normal colour vision.
- Therefore, the mother is heterozygous.
e.g. 3 2013 HKDSE IB (4a)
Red-green colour blindness is an X-linked recessive trait in humans. Peter is red-green colour blind while his daughter, Mary, is normal. Deduce Mary’s genotype without using a genetic diagram.
- As Mary’s father is red-green colour blind, he must have an X-chromosome bearing the recessive allele for red-green colour blindness.
- This X-chromosome must have been inherited to Mary.
- Genotype of female is XX. As Mary is normal, she must have at least one X-chromosome with the dominant normal allele for normal eye sight.
- Therefore, Mary is heterozygous.
e.g. 4 2013 HKAL II (4c)
In humans, a genetic disease D is caused by an allele located on the X chromosome. A couple, who are both without disease D, have given birth to a son with the disease. Based on this information, deduce the genotype of the mother and whether the allele for disease D is dominant.
- As the son has disease D, he must have an X-chromosome with the recessive allele for the disease.
- This X-chromosome must have been inherited from his mother.
- Genotype of female is XX. As the mother is normal, she must have at least one X-chromosome with the dominant normal allele.
- Therefore, the mother is heterozygous.
- Under heterozygous conditions, only the dominant allele will be expressed while the recessive allele will be masked. Since mother is normal, the allele for disease D is recessive.











Post a Comment
0 Comments