Type 2.2: 推斷一個trait 係dominant 定recessive (sex-linked)
再講2.2。解決呢類要記住兩句口訣。
1. 相生相剋
2. 異性相吸
兩句夾埋即係搵一pair 有吾同phenotype 既父女或母子。搵到之後就由男性做推斷再去到女性。
Formula of case 1:
- The father (the son) has the trait and being a male he has the genotype of XY. His X-chromosome must bear the allele for the trait on his only X-chromosome.
- This X-chromosome with the allele for the trait must have been inherited to the daughter (from his mother).
- Genotype of female is XX. The daughter (the mother) is normal in phenotype. Her other X-chromosome must bear the normal allele for manifestation of the normal phenotype.
- Hence, the daughter (the mother) is heterozygous.
- Under heterozygous condition, only the dominant allele will be expressed while the recessive allele will be masked. Hence, the allele for trait is recessive.
Formula of case 2:
- The father (the son) is normal and being a male he has the genotype of XY. His X-chromosome must bear the normal allele on his only X-chromosome.
- This X-chromosome with the normal allele must have been inherited to the daughter (from his mother).
- Genotype of female is XX. The daughter (the mother) has the trait. Her other X-chromosome must bear the allele for the trait for manifestation of the trait.
- Hence, the daughter (the mother) is heterozygous.
- Under heterozygous condition, only the dominant allele will be expressed while the recessive allele will be masked. Hence, the allele for trait is dominant.
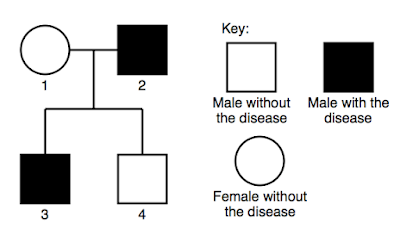
e.g. 1 2001 HKCE Human Biology I (3biii)
Without using a genetic diagram, deduce whether the allele for this disease is dominant or recessive.
- Individual 3 has the disease and being a male he has the genotype of XY. His X-chromosome must bear the defective allele on his only X-chromosome.
- This X-chromosome with the defective allele must have been inherited from individual 1.
- Genotype of female is XX. Individual 1 is normal in phenotype. Her other X-chromosome must bear the normal allele for manifestation of the normal phenotype.
- Hence, 1 is heterozygous.
- Under heterozygous condition, only the dominant allele will be expressed while the recessive allele will be masked. Hence, the defective gene is recessive.
e.g. 2 2010 May / June 9700 / 04 GCE AL IV (6b: modified)
The pedigree below shows the inheritance of a rare form of rickets caused X-linked allele.
Without using a genetic diagram, deduce whether the allele for this disease is dominant or recessive.
- 7 is normal and being a male he has the genotype of XY. His X-chromosome must bear the normal allele on his only X-chromosome.
- This X-chromosome with the normal allele must have been inherited to 9.
- Genotype of female is XX. 9 has rickets. Her other X-chromosome must bear the allele for the trait for manifestation of rickets.
- Hence, 9 is heterozygous.
- Under heterozygous condition, only the dominant allele will be expressed while the recessive allele will be masked. Hence, the allele for rickets is dominant.
呢條可以考慮 6 同 11.
e.g. 3 1993 HKAL II (1b)
The occurrence of colour blindness and haemophilia in a family is shown by the pedigree below. The alleles for the two traits are found on the X chromosome.
Deduce the dominance or recesssiveness of the allele which leads to
(1) Colour blindness
- Individual A has colour blindness and being a male he has the genotype of XY. His X-chromosome must bear the defective allele on his only X-chromosome.
- This X-chromosome with the defective allele must have been inherited to individual D.
- Genotype of female is XX. Individual D is normal in phenotype / not colour blind. Her other X-chromosome must bear the normal allele for manifestation of the normal phenotype.
- Hence, D is heterozygous.
- Under heterozygous condition, only the dominant allele will be expressed while the recessive allele will be masked. Hence, allele for colour blindness is recessive.
(2) Haemophilia
- Individual C has haemophilia and being a male he has the genotype of XY. His X-chromosome must bear the defective allele on his only X-chromosome.
- This X-chromosome with the defective allele must have been inherited to individual F.
- Genotype of female is XX. Individual F is normal in phenotype. Her other X-chromosome must bear the normal allele for manifestation of the normal phenotype.
- Hence, F is heterozygous.
- Under heterozygous condition, only the dominant allele will be expressed while the recessive allele will be masked. Hence, allele for haemophilia is recessive.













Post a Comment
0 Comments